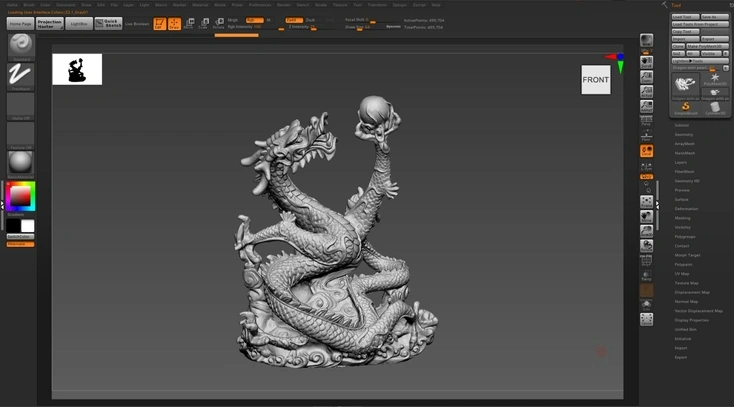
Unlocking the Potential of Low Poly 3D Models in Various Industries
by Animatics Asset Store in Blog on August 21, 2024The landscape of 3D modeling has evolved dramatically, impacting numerous sectors from product design to entertainment through digital prototypes, interactive simulations, and enhanced visualizations. This dynamic shift towards digitalization underscores the growing significance of low poly 3D models in today’s tech-driven world. These models are distinguished by their minimalistic design, which uses fewer polygons, thereby balancing visual quality with computational efficiency. This balance is particularly crucial in real-time applications such as gaming and augmented reality (AR), where performance and fluidity are paramount.
Understanding Low Poly 3D Models
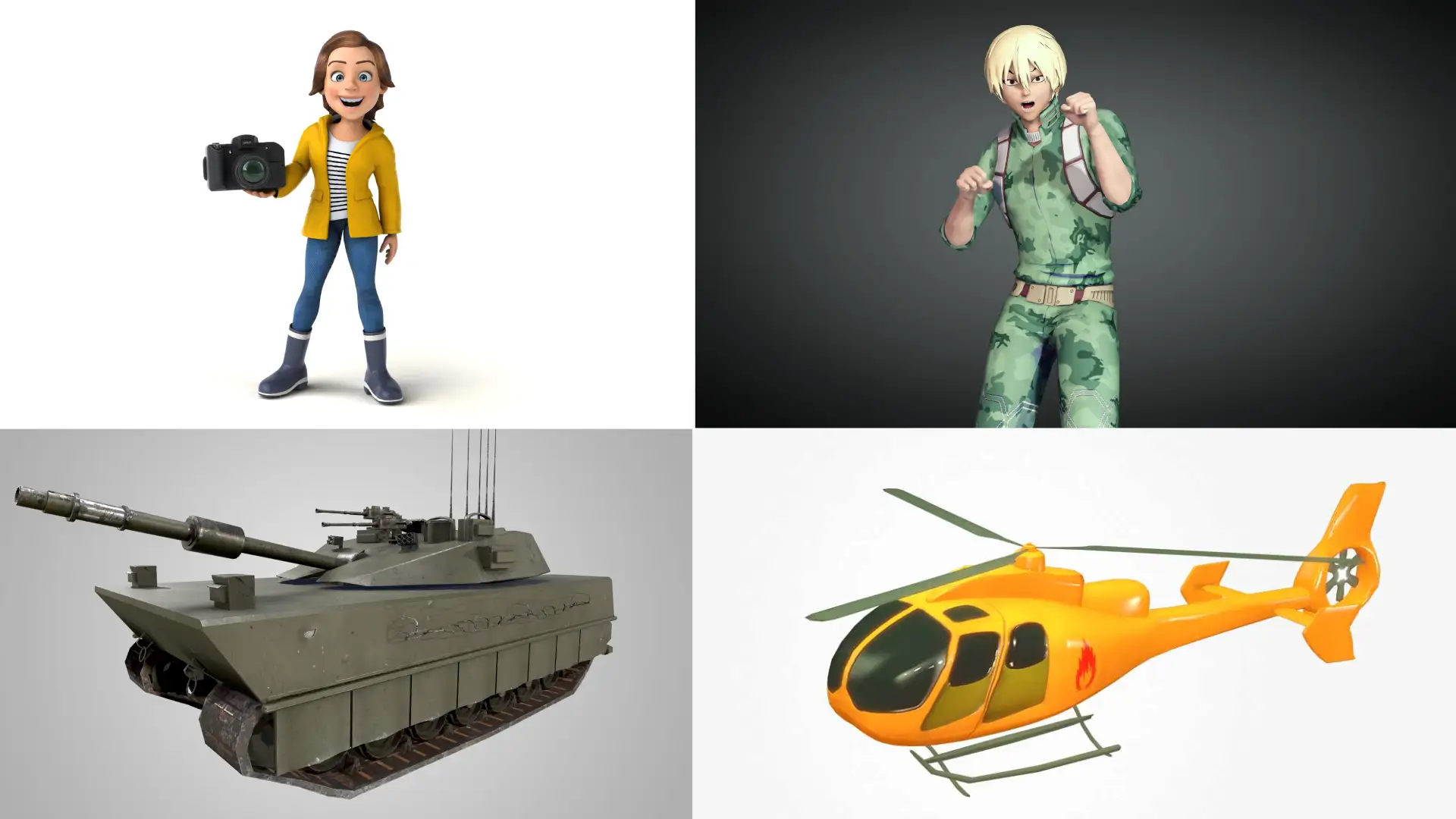
Low poly 3D models are defined by their simple geometric shapes and a reduced polygon count, typically ranging from a few hundred to several thousand. This streamlined structure not only accelerates rendering processes across various platforms but also enhances application performance, making these models a staple in the gaming and VR industries.
Core Aspects of Low Poly Modeling
Polycount Management:
The essence of low poly models lies in their efficient use of polygons to depict objects. This efficiency allows for faster processing and smoother performance without compromising the aesthetic or functional integrity of the model. For example, while a shiny metallic surface might require a higher polycount to reflect its luster accurately, simpler objects like the Leaning Tower of Pisa can be effectively represented with fewer polygons.
Optimization Techniques:
Key techniques like edge loops and polygon merging are employed to maintain surface smoothness and reduce visual artifacts, ensuring that the models are both lightweight and high in quality. Optimization also involves the elimination of unnecessary vertices and the simplification of textures without detracting from the desired shape.
Essentials of Low Poly Modeling
The creation of low poly 3D models involves careful consideration of polycount, which directly influences the model’s complexity and performance impact. The range for what constitutes a low poly model can vary widely, but typically includes models with up to 10,000 polygons. This approach is advantageous not only for maintaining performance but also for ensuring that the models are not overly taxing on hardware resources.
- Polycount Considerations: The number of polygons in a model dictates its detail and visual richness. For instance, simpler objects in a scene, such as background elements, can effectively use fewer polygons without compromising the overall aesthetic.
- Optimization Techniques: Key techniques in crafting low poly models include optimizing edge flow to maintain smoothness and utilizing polygon reduction strategies without losing essential form. These strategies are critical in keeping the models lightweight and performance-friendly.
- Retopology and Decimation: These processes are vital for refining the geometry of a model. Retopology involves redefining mesh topology with fewer polygons, essential for animation and texture mapping, while decimation reduces the polygon count without significantly altering the model’s appearance.
- UV Mapping and Texturing: Efficient UV mapping is crucial for applying textures to a model without distortion. Textures add necessary visual details that might be lost when reducing the polygon count.
- Normal Mapping and Baking: These techniques allow low poly models to appear more detailed without the computational overhead of additional polygons. Baking transfers details from high-poly models to low-poly versions, effectively embedding texture and light information.
Applications in Gaming and Virtual Reality
Low poly 3D models are integral to developing interactive environments in gaming and virtual reality. Their reduced complexity allows developers to create expansive, detailed worlds that are accessible on a wide range of hardware, from high-end gaming consoles to mobile phones.
- Efficient Real-Time Rendering: For real-time applications, low poly models are optimized to reduce the load on graphics processors, ensuring smooth frame rates and responsive gameplay or VR experiences.
- Level of Detail (LOD) Systems: Implementing LOD systems helps in managing model complexity in real-time. As the viewer moves away from an object, the system swaps high-detail models for lower-detail counterparts, conservatively using system resources.
Extending to AR and Cinematic Use
In augmented reality, low poly models blend digital objects with the real world smoothly and efficiently, enhancing user engagement without overloading the device’s capabilities. In cinema, particularly in animated features or VFX-heavy films, low poly models are employed for background characters and environments to effectively manage rendering budgets.
The Role in E-commerce and 3D Printing
E-commerce platforms benefit from low poly models through faster page loads and smoother previews of products, enhancing user experience and engagement. In 3D printing, low poly models are favored for their simpler geometry, leading to fewer printing errors and reduced material use. This makes the printing process more efficient and cost-effective.
Conclusion
Low poly 3D models showcase versatility across platforms, meeting modern digital demands. They enhance gaming experiences, enable efficient AR interactions, and streamline 3D printing processes. These models balance performance optimization with visual quality, demonstrating their strategic utility. Industries adopting low poly techniques can ensure smoother operations and tap into new markets and opportunities. This approach pushes the boundaries of what is possible in the digital realm.